The Internet now exists as a rigidly centralized pyramid of domain names and addresses, built on top of a decentralized network of interconnected numerous independent information nodes and sites.
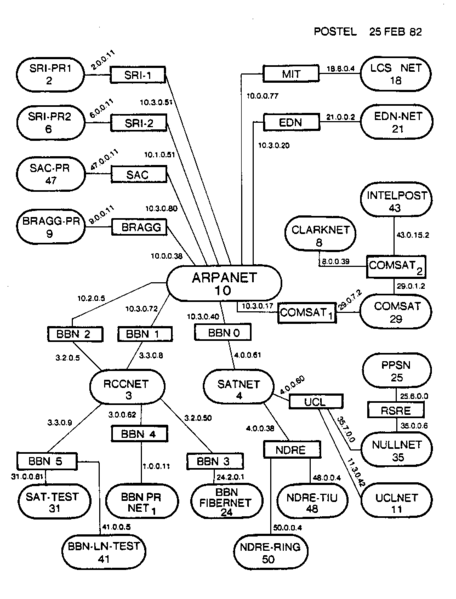
The Internet hierarchical system was established by Jon Postel from Stanford Research Institute in years 1982-1983 to replace his overweight phone book containing names and numbers of all connected nodes.
The World Wide Web as the predominant form of information storage and a browser as a tool for remote access to it were developed by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1991.
Social Networks and Messengers are main forms of communication in the Internet. About half of all the Earth population use them.

SHORT TIMELINE:
1965 US Department od Defence (ARPA) connected 2 computers through telephone line
1967 International Management Systems Association changed its name to INTERNET. In 1994 it changed its name again to International Project Management Association (IPMA) not to be confused with actual Internet.
1969-1971 2, then 3, then 15 American institutes and military bases permanently connected their computers
1971 1st email, i.e. piece of information with header "user@host" was sent by Ray Tomlinson of ARPANET
1974 the word INTERNET first mentioned in RFC-675 as short name of Internetwork Transmission Protocol
1980-1984 Usenet, CSNet, BITNet, FIDONet, Russian Academnet, French Minitel based on different technologies were established
1982-1983 Jon Postel from Stanford Research Institute (SRI) digitalised his sketchpad with names and addresses of 38 interconnected networks and computers and suggested it be universal Inter-Network Phonebook with TCP-IP (ARPA) as preferred protocol, DNS as system of addressing and SRI as World hub for every network.
1989-1991 commercial Internet-providers suggested Internet-access for everybody in USA, Europe and USSR
1991 Tim Berners-Lee of CERN introduced WordWideWeb (WWW) as decentralized hypertext-based information storage and released 1st browser to see it.